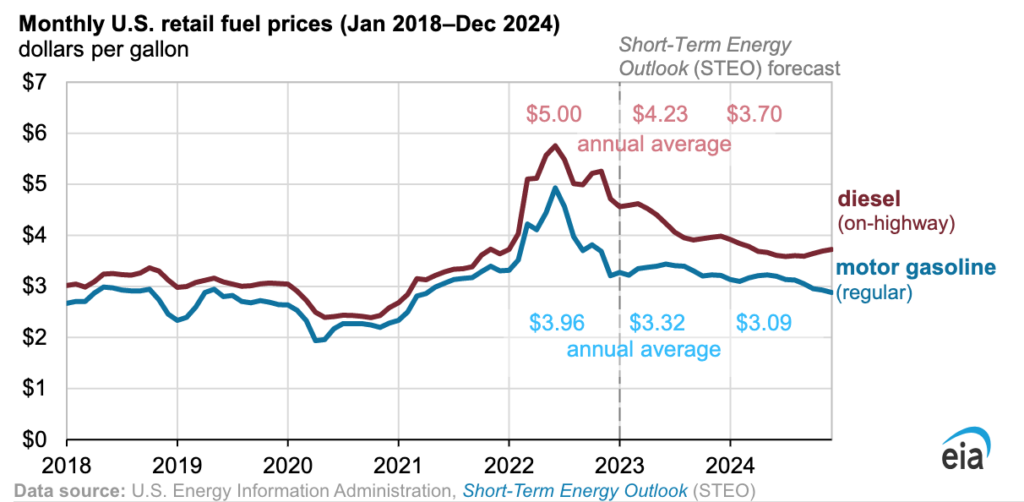
The latest Short-Term Energy Outlook predicts a decline in retail gasoline and diesel prices in 2023 and 2024 after reaching multiyear highs in the first half of 2022. Regular-grade gasoline prices are expected to average $3.32/gal in 2023 and $3.09/gal in 2024, while on-highway diesel prices are expected to average $4.23/gal in 2023 and $3.70/gal in 2024.
In short, refinery capacity expansions and increased gasoline and diesel production could contribute to rising supplies and lower prices globally in 2023 and 2024.
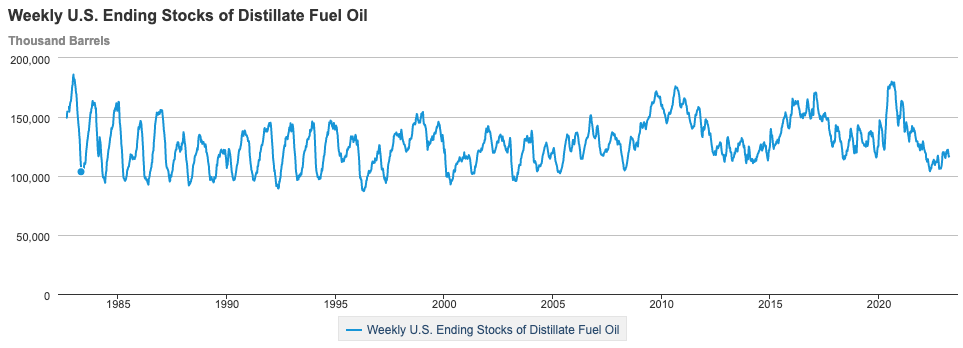
Diesel Inventories
Recent reports indicated that diesel inventories in the United States were decreasing and had reached critically low levels. However, the Energy Information Administration (EIA) has reported only a 13% decrease in inventories compared to the previous five-year average.
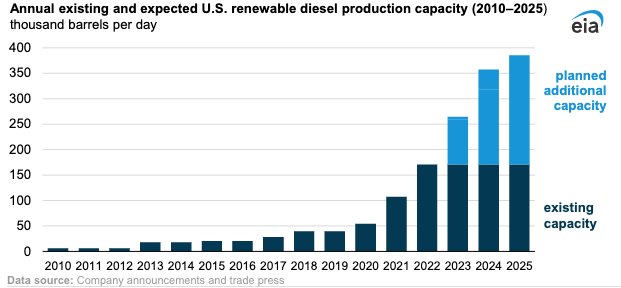
Diesel Production
As the industry is recovering from diesel price fluctuations in the United States due to fluctuations in international oil supply, transportation challenges, and geopolitical affairs causing turmoil and uncertainty in the market, there are two leading factors behind the growing U.S. renewable diesel capacity. Rising targets for state and federal renewable fuel programs and biomass-based diesel tax credits.
The renewable diesel industry in the US has seen significant growth, with 16 plants in operation by the end of 2022, including six new plants that began operation during the year. Most of these plants are converted from existing petroleum refineries, and only a few are completely new facilities. The total nameplate production capacity of all plants was 2.6 billion gallons in 2022, with the two largest plants capable of producing at least four times more fuel than the top two biodiesel plants.
Petroleum Imports
The US is the world’s second-largest importer of crude oil after China, importing more than 8 million barrels of petroleum products daily from other countries. Canada is the largest source of petroleum imports for the US, providing over 51% of US petroleum imports in 2021, and 62% when counting only crude oil imports.
Mexico is the second-largest contributor to US petroleum imports, providing slightly over 8% of US petroleum imports with 259 million barrels imported in 2021. Russia is the third-largest exporter of crude oil and petroleum products to the US, providing almost 8% of total imports with 254 million barrels in 2021.
Renewable Diesel Production
A number of former petroleum refineries are intending to initiate the production of renewable biodiesel in the years to come. One of them is Marathon Petroleum’s refinery located in Martinez, California, which commenced production of renewable diesel in 2022 and could achieve its maximum production capacity of 730 million gallons per year (48,000 barrels per day) in 2023. As well as Phillips 66’s Rodeo Renewed project located in San Francisco, California, which is aiming to generate 800 million gallons per year (52,000 barrels per day) of renewable fuels upon its complete conversion in 2024. If this target is met, this facility would become the largest of its kind in the world.
Renewable diesel production involves making biodiesel from vegetable oils or animal fats. FAME (Fatty Acid Methyl Ester) is a type of biodiesel created through a chemical reaction called transesterification, which converts the oil or fat into FAME and glycerol. The purified FAME is blended with diesel fuel and can be used in various proportions depending on the country and fuel standards. Biodiesel and FAME plants are the same thing and produce biodiesel using transesterification. The term “FAME plant” is sometimes used to differentiate between those that produce FAME biodiesel and those that produce other types of biodiesel.


